Is Stainless Steel Stainless ?
Joining two metal junctions or fusing them is a very common practice in fabrication for various applications. Major two groups are Fusion Welding and Solid state welding.
Base metal is melted by means of heat. In fusion welding process a filler material is added to provide bulk and strength to the joint, known fusion methods are arc welding, resistance welding, oxy-fuel welding, electron beam welding. In Solid state welding the joints are welded by applying pressure alone or pressure with heat in combination. In solid state welding filler material will not be used. Diffusion welding, Friction welding and Ultrasonic welding are the know methods. Both these techniques have the pro’s and con’s which are used for different applications.
Passivation of Stainless Steel:
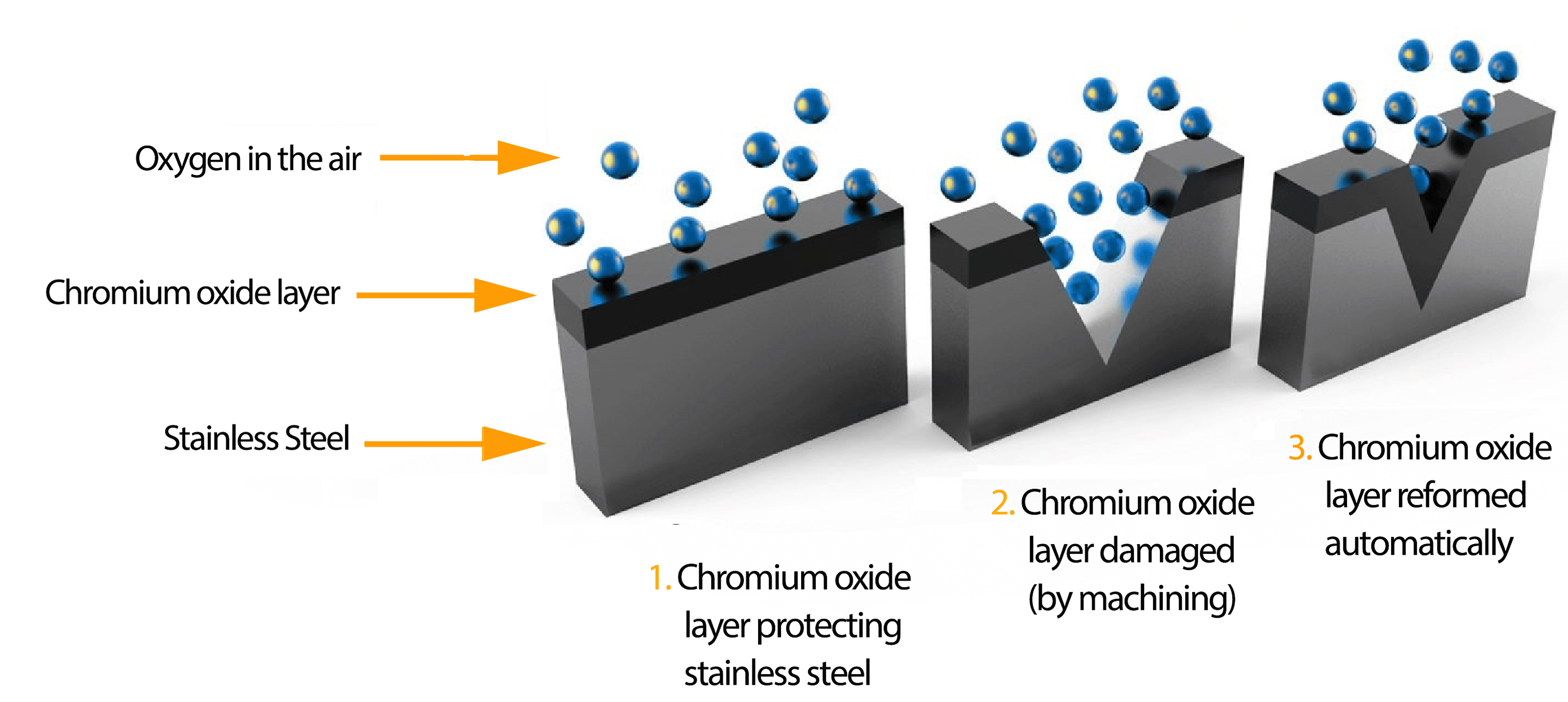
Fig 1: Passivation Process [1]
Most of the fabricators use TIG Welding for Stainless Steel, as this method is very easy to fabricate and low cost compared to other techniques, this method will use filler material which is again SS with different grades which suits applications, considering the challenges we need to address while we use TIG welding for the stainless steel fabrication are wide and cumbersome, matching the right filler material for the base SS material, using the right temperature, else high temperatures can cause porosity, Dirt, grease and moisture should be removed by cleaning the surface to remove oxides else we will again experience porosity, lack of fusion is another problem even though we have explained these issues skill can overcome these, also enormous amount of energy used for welding will leave heat tint on the weld joints which has to be properly removed else the surface will not be exposed for passivation which is another challenge, nevertheless we have good weld strength, but we need to remove the heat tint and expose the material to oxidize to let Stainless steel be stainless. The percentage of Chromium in SS alloy will determine the corrosion resistance property and also determines the time taken for passivation (as shown in Fig:1 [1] )after removal of heat tint, higher the % of Cr (>25% and <30%) faster the passivation (10 to 12 Hours), a minimum of 10.5% Cr is needed to enable passivation, usually 24 to 48 Hours is need to enable passivation.
Methods to remove Heat Tint:
To enable passivation we have many methods like sandblasting, pickling, scrubbing, chemical treatment by using harsh chemicals. Advanced methods like electro-chemical cleaning and electropolishing will expose the chrome layer to environment to enhance the passivation and also lets the steel luster.
Most of the industries uses pickling as one of the convenient method to remove the heat tint, upon many existing techniques as it is very simple and cost effective method, but the only disadvantage is the valley’s and the peaks of the weld area are not completely cleaned.
Alternate techniques are Electro-chemical methods for removal as they are very efficient by using right mixture of chemicals at the right temperature with a brush to scrub and dispense the chemical and expose the chrome to enable passivation.
Techniques to measure Passive Layer:
We can also employ different methods to check if the passivation or the oxide layer is formed or not, a recent technology measures conductivity of two points by applying current, higher the value higher the passive layer thickness which avoids corrosion.
These techniques lets the user and the engineer rule out the first suspicion of rusting but passivation makes stainless steel stainless !
Reference:
[1] https://www.nitty-gritty.it/stainless-steel-passivation-process/?lang=sv
For more information download our company brochure.
Check our blogs

